Understanding Vascular Conditions
What is a Vascular Specialist?
A vascular specialist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the blood vessels. These blood vessels include arteries, veins, and lymphatic vessels.
Vascular specialists have extensive training in the body's circulatory system. This allows them to provide comprehensive care for all vascular conditions, using a variety of medical, minimally invasive, and surgical treatments. The rigor and depth of their training make them uniquely qualified to evaluate and restore vascular health. Their expertise spans medical management, imaging interpretation, endovascular procedures, bypass grafting, and conventional surgery.
When you are experiencing any disorder that impacts blood flow or vascular function, it is important to see a board-certified vascular specialist promptly. This will help to preserve circulation and prevent severe complications.
When to See a Vascular Specialist
You should schedule an appointment with a vascular surgeon promptly if you experience any symptoms or health concerns that may indicate an underlying blood vessel disorder. Getting specialized vascular care early is crucial for proper diagnosis and effective treatment. If you experience any of the following symptoms, it is important to see a vascular specialist:
- Leg pain and swelling
This can be a sign of deep vein thrombosis (DVT), chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), or other vascular conditions. - Non-healing wounds
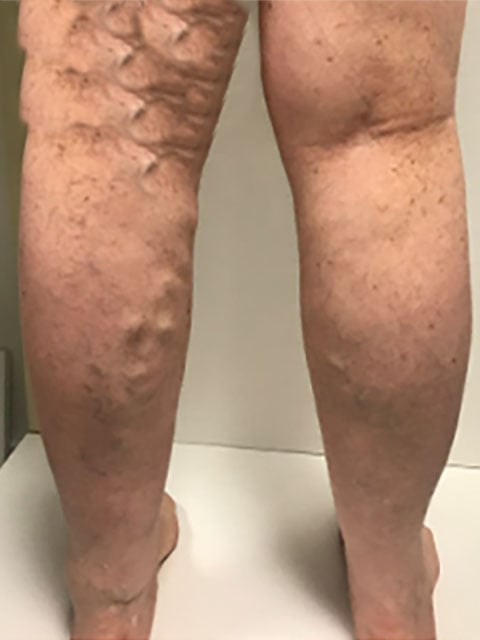
Wounds or ulcers on your legs or feet that don't heal or take a long time to heal may be a sign of poor blood circulation. - Varicose veins
Bulging and twisted veins often seen in the legs can sometimes indicate underlying venous insufficiency, which may require medical attention. - Chest pain
Chest pain can be a symptom of various cardiovascular conditions, including those affecting the blood vessels. It's important to rule out any vascular-related issues. - High blood pressure
Uncontrolled high blood pressure can damage blood vessels over time, increasing the risk of various vascular disorders. - Family history
If you have a family history of vascular diseases, you may be at a higher risk and should consider regular check-ups. - Risk factors
Having risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, obesity, and a sedentary lifestyle can increase your chances of developing vascular problems. - Prior vascular conditions
If you have been previously diagnosed with a vascular condition, regular follow-ups with a vascular specialist are crucial for monitoring and management.
Vascular Diagnostic Tests
Accurate diagnosis is the cornerstone of effective vascular care. Your vascular specialist will determine which diagnostic tests are most appropriate based on your symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. These tests play a vital role in uncovering underlying vascular issues, guiding treatment decisions, and improving overall vascular health. Here are some common vascular diagnostic tests:
- Doppler Ultrasound
This non-invasive test uses sound waves to create images of blood flow in the arteries and veins. It's commonly used to diagnose conditions like deep vein thrombosis (DVT), peripheral artery disease (PAD), and varicose veins. - Duplex Ultrasound
A combination of traditional ultrasound and Doppler ultrasound, this test provides both visual images and real-time blood flow data. It's particularly useful for assessing blood vessel narrowing, clots, and valve function. - Angiography
This x-ray-based test involves injecting a contrast dye into the blood vessels to visualize the blood flow. It's helpful in diagnosing blockages, aneurysms, and other abnormalities. - CT Angiography (CTA)
Computed tomography (CT) scans combined with contrast dye create detailed images of blood vessels, aiding in the diagnosis of arterial conditions. - Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA)
This non-invasive imaging technique uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create images of blood vessels. It's particularly valuable for assessing the arteries in detail without using X-rays. - Arterial Plethysmography
This test measures blood pressure at various points along the arteries, helping identify blockages and assess blood flow. - Venous Plethysmography
Similar to arterial plethysmography, this test evaluates blood flow in the veins, assisting in the diagnosis of conditions like varicose veins and venous insufficiency. - Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI)
This test compares blood pressure measurements in the arms and legs to assess the presence of peripheral artery disease. - Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA)
An advanced form of x-ray angiography, DSA provides real-time images of blood vessels during the injection of contrast dye, aiding in the detection of abnormalities.
Vascular Procedures and Treatment Options
Vascular health is essential for overall well-being. When issues arise within the circulatory system, there are a variety of advanced procedures and treatments available to address them. Vascular specialists employ cutting-edge techniques to ensure optimal blood flow and prevent potentially serious complications. Here are some key vascular procedures and treatment options:
- Pedal loop angioplasty
This minimally invasive procedure is used to treat peripheral artery disease (PAD) by opening up narrowed or blocked arteries in the lower extremities. A balloon-tipped catheter is inserted through a small incision and inflated to widen the artery, restoring proper blood flow and alleviating symptoms such as leg pain and cramping. - Vein ablation
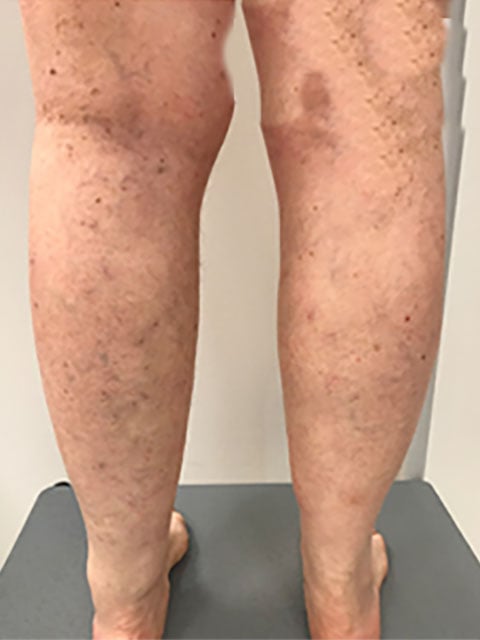
Vein ablation is a technique used to treat varicose veins and chronic venous insufficiency (CVI). Through minimally invasive methods like radiofrequency or laser ablation, the damaged vein is sealed, redirecting blood flow to healthier veins and improving circulation. - DVT treatment
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot forms within a deep vein, often in the legs. Timely treatment is crucial to prevent the clot from breaking free and causing a pulmonary embolism. Therapies may include anticoagulant medication, catheter-based techniques to remove the clot, and compression stockings to improve blood flow. - PE treatment
Pulmonary embolism (PE) arises when a blood clot travels to the lungs, potentially causing breathing difficulties and even death. Treatment involves anticoagulant medication to prevent further clot formation, along with supportive measures to stabilize the patient's condition. - Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) treatment
CVI occurs when the veins struggle to send blood from the legs back to the heart. Treatments may include lifestyle changes, compression stockings, and minimally invasive procedures to improve vein function and reduce symptoms like swelling and discomfort.
Photo Gallery
Video Gallery
Testimonials
She made me feel like I was the most important person she could be taking care of.
Thanks to both of you it was a pleasant experience with absolutely no anxiety at all.
Dear Linda & Michelle: I wanted to thank you both for your excellent care given to me yesterday, when I was in your office for my PET scan. From the moment I arrived you explained everything to me in perfect detail so there were no “surprises” at all and I knew exactly what to expect. Kudos to you Linda for finding a vein for the IV right away! Michelle, you were very reassuring and by the way…you make good coffee!!!
I had my life back.
Doctor Dilip Viswanath made the recommendation that I start EECP therapy. I hugged the wall down the hall to my first session. I was able to walk back slow but without help. I felt better with each passing day. I had my life back. I have my freedom again and am able to drive again. I still have medical problems that are also being addressed but look at me now.
I felt as if I was the only one that mattered!
With the volume of people you serve, it would be so very easy to just “get them in and get them out,” but that was not the case. I felt as if I was the only one that mattered! So please extend my thanks and appreciation to your very excellent, professional and courteous staff.